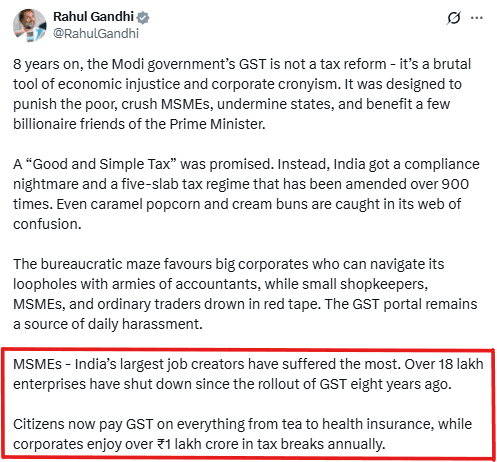
Claim: A tweet by Rahul Gandhi claims that 18 lakh+ Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) have shut down since 2017 due to difficulties posed by Goods and Services Tax (GST). He further claims that consumers are now paying GST on tea and health insurance, thus implying there was no tax on these products before GST.
Our examination found the claim to be FALSE.
How We Examined the Claim:
1. We analyzed MSME registration and closure details from various government sources from the year 2010-11 to 2024-25.
| Year | Registered MSMEs | MSMEs Closures |
| 2017-2018 | 15,16,908 | 0 |
| 2018-2019 | 21,19,744 | 0 |
| 2019-2020 | 25,62,258 | 245 |
| 2020-2021 | 40,12,281 | 330 |
| 2021-2022 | 51,35,627 | 6,222 |
| 2022-2023 | 85,64,767 | 13,290 |
| 2023-2024 | 2,49,12,531 | 19,828 |
| 2024-2025* | 64,86,029 (as on 05.08.2024) | 35,567( as on 28.02.2025) |
| Total | 5,53,10,145 | 75,482 |
Source: Source: Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises. (2020, June). Registration of micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in India [PDF]. Government of India, Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises. (2024, March 13). Number of MSMEs registered on Udyam portal [Unstarred Question No. 2952, Lok Sabha]. Government of India, Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises. (2024). Data on MSME registrations and closures from 1 May 2017 to 2020 [Unstarred Question No. 1398, Lok Sabha]. Government of India, Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises. (2023, July 24). Financial year-wise data on MSME closures in India [Unstarred Question No. 85, Lok Sabha]. Government of India, Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises. (2023). Details of Udyam registrations and closures [Unstarred Question No. 1855, Lok Sabha]. Government of India.
GST was introduced in the year 2017. From the table, we can see that since introduction of GST, 75,482 MSME’s have closed down.
We also see that 55,310,145 MSME’s were registered in the same period. In the 7 years prior to GST introduction (that is 2010-11 to 2016-17), only 4,709,180 (References 1 and 2). MSME’s had registered. This indicates over 1000% jump in MSME registrations after the introduction of GST.
2. We reviewed Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) Press Release that provides pre-GST and post-GST tax rates for tea. We also reviewed Union Budget 2016-17 for Service Tax rate on health insurance. We found that both tea and health insurance were taxed in the pre-GST indirect tax regime too. Due to GST slab rationalization on products and services, GST rates either slightly went up or down relative to pre GST indirect tax rates. Tax on tea fell from 7 to 8% pre- GST to 5% under GST regime. On the other hand, tax on health insurance went up from 15% pre-GST to 18% under GST regime (Ref 9). This indicates normalization of tax rate slabs and not a new tax.

Conclusion:
Rahul Gandhi has not provided any source for his claim that 18 lakh+ MSMEs have shut down since the introduction of GST. Official data shows that actual MSME closures since GST rollout is only a fraction of that claim (75,482 against claim of 18 lakh). The numbers do not indicate difficulty in business post GST, in fact, MSME registrations post GST have gone up 10 times. Additionally, official data shows that both tea and health insurance were taxed prior to introduction of GST as well.
Therefore, the claims are False.
References:
- Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises. (2016). MSME annual report 2015–16 [Annual report]. Government of India. https://msme.gov.in/sites/default/files/MEME%20ANNUAL%20REPORT%202015-16%20ENG.pdf
- Development Commissioner (MSME). (2020, June). Udyog Aadhaar Memorandum – Registration of MSMEs in India. Ministry of MSME. https://www.dcmsme.gov.in/Uampulication-june2020.pdf
- Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises. (2020, June). Registration of micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in India [PDF]. Government of India. https://www.dcmsme.gov.in/Uampulication‑june2020.pdf
- Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises. (2024, March 13). Number of MSMEs registered on Udyam portal [Unstarred Question No. 2952, Lok Sabha]. Government of India. https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/182/AU2952_2aoSQa.pdf
- Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises. (2024). Data on MSME registrations and closures from 1 May 2017 to 2020 [Unstarred Question No. 1398, Lok Sabha]. Government of India. https://sansad.in/getFile/annex/258/AU1398.pdf
- Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises. (2023, July 24). Financial year-wise data on MSME closures in India [Unstarred Question No. 85, Lok Sabha]. Government of India. https://sansad.in/getFile/loksabhaquestions/annex/1712/AU85.pdf
- Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises. (2023). Details of Udyam registrations and closures [Unstarred Question No. 1855, Lok Sabha]. Government of India. https://sansad.in/getFile/annex/267/AU1855_evURwk.pdf
- Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs. (2017, July 3). Comparative analysis of the proposed GST tax rates to the prevailing taxes on important commodities [Press release]. Government of India. https://cbic-gst.gov.in/pdf/press-release/analysis-gst-rates.pdf
- Union Budget 2016-17




