1. What is the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT)?
The Indus Waters Treaty (IWT), signed on September 19, 1960, is a water-sharing agreement between India and Pakistan, brokered by the World Bank. It divides six rivers:
- India controls: Ravi, Beas, Sutlej (Eastern Rivers).
- Pakistan controls: Indus, Jhelum, Chenab (Western Rivers).
The treaty allowed both countries to use their allocated rivers peacefully, even during wars and conflicts. It became a symbol of cooperation despite political tensions.
2. Why Did India Suspend the Treaty in 2025?
On April 22, 2025, a terrorist attack in Pahalgam, Jammu & Kashmir, killed 26 Indian civilians. India blamed Pakistan for supporting terrorism. As a response, India suspended the Indus Waters Treaty on April 23, 2025.
This action was historic because, for the first time in 65 years, the treaty was paused, raising concerns about water security and regional stability.
3. Timeline of the Indus Waters Treaty
| Date | Event |
| 1947 | Partition of British India creates water disputes over the Indus system. |
| April 1948 | India halts water flow after Standstill Agreement expires. |
| May 4, 1948 | Inter-Dominion Accord restores water flow in exchange for payments. |
| 1954 | World Bank offers to mediate the dispute. |
| 1954–1960 | Lengthy negotiations under World Bank supervision. |
| Sept 19, 1960 | Indus Waters Treaty signed by Nehru and Ayub Khan. |
| 1965 | Treaty survives First Indo-Pakistani War. |
| 1971 | Treaty remains during Second Indo-Pakistani War. |
| 1999 | Treaty holds firm during Kargil conflict. |
| 2017 | Tensions rise over India’s Kishanganga Dam project. |
| April 22, 2025 | Terrorist attack in Pahalgam kills 26 civilians. |
| April 23, 2025 | India officially suspends the Indus Waters Treaty. |
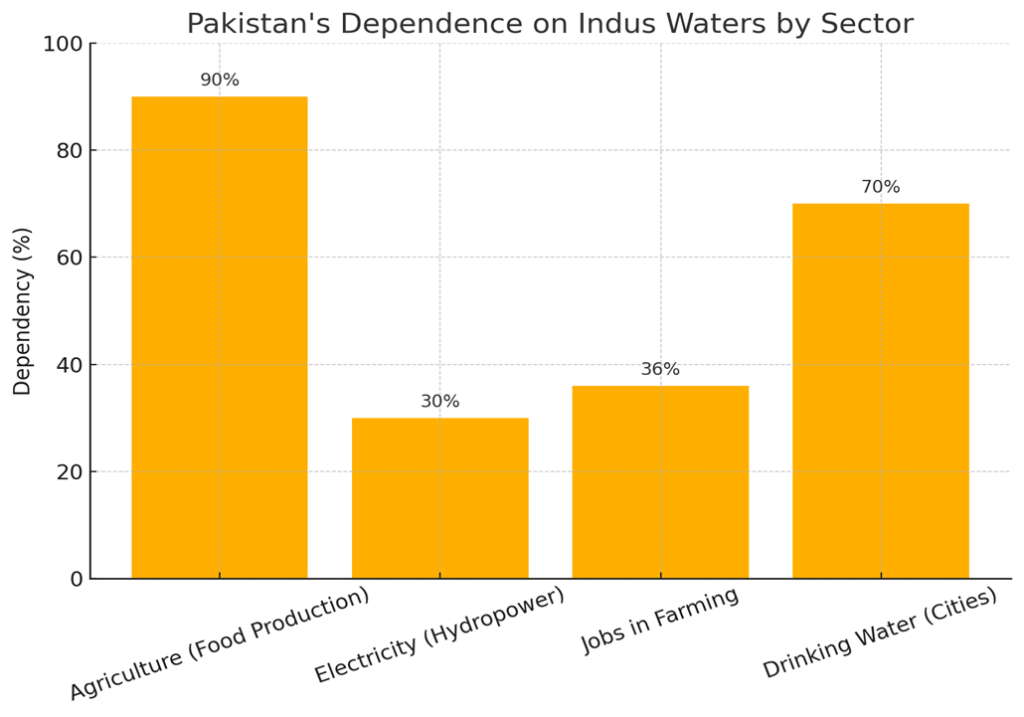
4. Why is Water So Important for Pakistan?
Pakistan’s survival depends heavily on the Indus River system:
| Sector | Dependency on Indus Waters |
| Agriculture | Irrigates 80% of farmland |
| Food Supply | Supports 90% of production |
| Electricity | Provides 23-30% via dams |
| Jobs | ~36% workforce in farming |
| Drinking Water | Major cities rely on rivers |
What Happens If Water Stops?
- Less food → Higher prices → Hunger
- Less electricity → Power cuts → Factory shutdowns
- Less water → Cities suffer → Protests & unrest
Pakistan’s Dependence on Indus Waters:
5. India’s Gains & Challenges:
| India’s Potential Gains | Challenges India Faces |
| Control over more water | Expensive dams & infrastructure needed |
| Strategic pressure on Pakistan | Risk of international criticism |
| More irrigation & hydropower | Rising tensions with Pakistan |
India can use more water from the Western Rivers but will need years of investment to fully benefit.
6. Economic Impact Summary
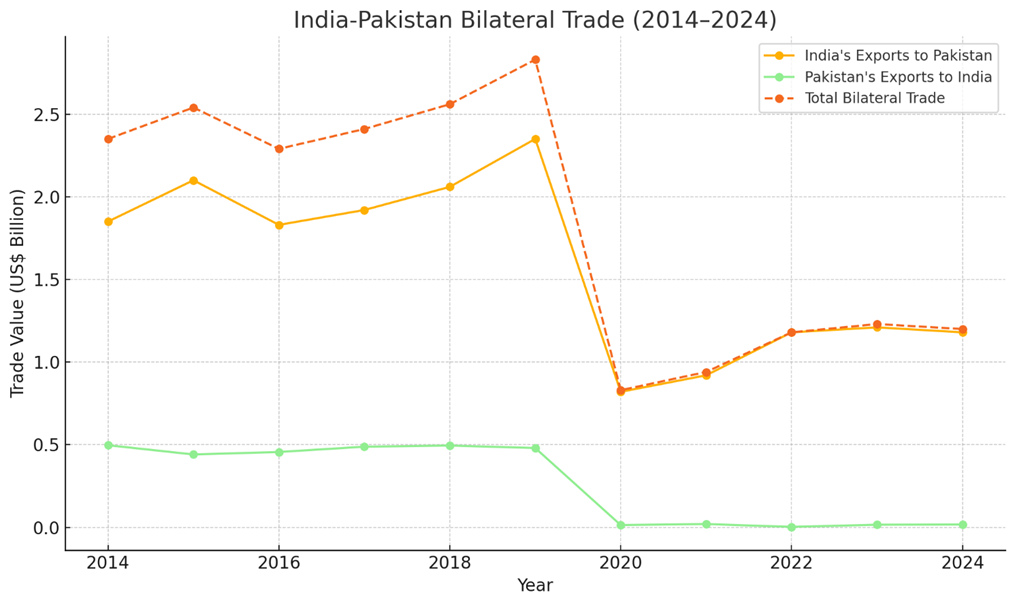
India-Pakistan Bilateral Trade (2014–2024)
Trade between India and Pakistan has been declining due to political tensions:
| Year | Total Trade (US$ Billion) |
| 2014 | 2.35 |
| 2018 | 2.56 |
| 2019 | 2.83 (Peak) |
| 2024 | 1.20 (Before Suspension) |
By 2024, trade had dropped to just $1.20B, mostly India exporting goods to Pakistan.
India-Pakistan Trade Collapse (2014–2024)
Conclusion:
- The Indus Waters Treaty suspension is a turning point in India-Pakistan relations.
- Pakistan faces serious risks to its food security, electricity supply, and economic stability due to its heavy reliance on Indus waters.
- India gains strategic control over water resources but must handle infrastructure costs and global diplomatic challenges.
- Bilateral trade, already weakened, has now come to a complete halt after years of decline.
- The suspension increases the likelihood of long-term economic hardship and rising tensions between the two nations.
References:




